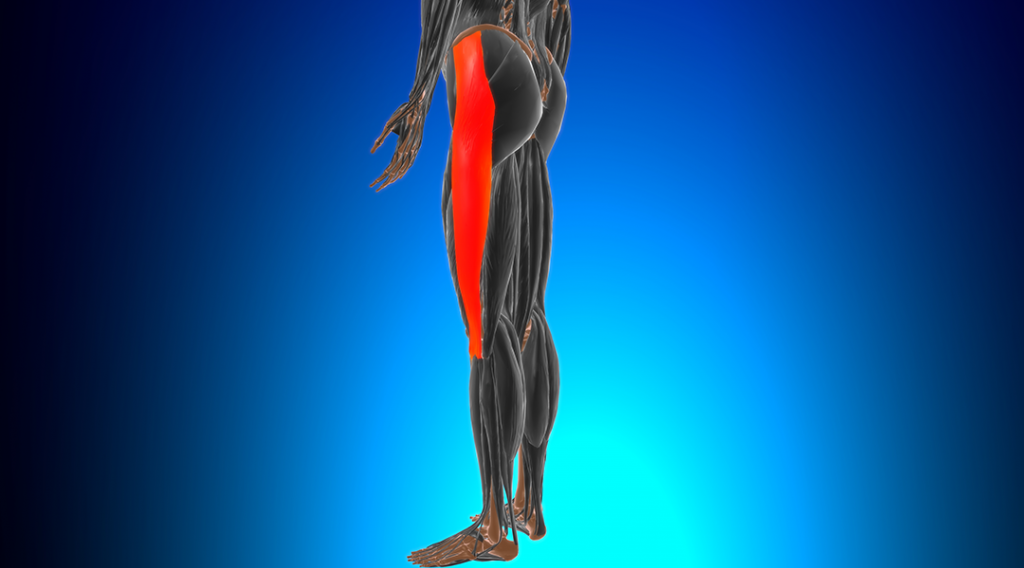
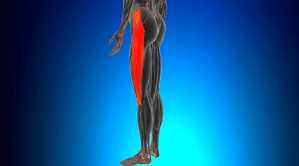
Iliotibial band syndrome occurs when the iliotibial band gets irritated or swollen from rubbing against your hip or knee bones. The tendon spans the outside of your thigh from the top of your pelvic bone down to your knee. Typically, you are at greater risk for developing iliotibial band syndrome if you’re young and exercise frequently.
There are many underlying factors that can contribute to developing iliotibial band syndrome including knee arthritis, weakness in your hip or core muscles, patellofemoral pain syndrome, or even ligament tear. Structural and functional impairments that may also lead to iliotibial band syndrome include excessive foot pronation, hip abductor weakness, and tibial torsion,
People with iliotibial band syndrome describe the initial pain as aching and burning. The more they exercise their leg, and the worse the syndrome gets, the sharper the pain turns. Possible causes to iliotibial band syndrome also include: cooling down too quickly after performing an exercise, warming up too quickly or not stretching enough before an exercise, or a lack of rest,
The Most Common Signs & Symptoms of Iliotibial Band Syndrome
- Aching, burning, or tenderness on the outside of your knee
- Clicking , popping, or snapping on the outside of your knee
- Warmth and redness on the outside of your knee
(Source: Cleveland Clinic)
What Are the Treatments for Iliotibial Band Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome?
Marcel Jacobs PT provides a hands-on physical therapy approach which means you’re going to get fast access to immediate care in order to soothe and relax those tight and aching muscles, mobilize and loosen those restricted and painful joints, and strengthen your body so that you can go back to doing the things that you love. Your therapist will perform a thorough physical examination and evaluation in order to provide you with a deeper understanding of your impairments, compensations, and dysfunctions. You may find yourself having your concerns eased, questions answered, and physical pain reduced inside of 45 minutes with your physical therapist.